How to Calculate Area of Triangle in Java
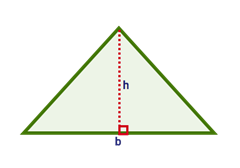
Area of any type of triangle can be calculated using the formula, Area = (b*h)/2, where b is the base of the triangle and h is the vertical height. The following diagram shows how to define base and vertical height of a triangle.
The following sample Java program calculates the area of a triangle given its base and vertical height. Note that this approach works for any triangle.
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* Calculates area of triangle in Java given its base and vertical height.
* @author jj
*/
public class AreaOfTriangle1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sn = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter base of triangle:");
double base = sn.nextDouble();
System.out.println("Enter vertical height of triangle:");
double verticalHeight = sn.nextDouble();
AreaOfTriangle1 at = new AreaOfTriangle1();
double area = at.calculateArea(base,verticalHeight);
System.out.println("Area = "+area);
}
/**
* Calculates area of a triangle using base and vertical height
* @param base
* @param verticalHeight
* @return
*/
private double calculateArea(double base, double verticalHeight) {
return base*verticalHeight/2;
}
}
However if you don't know base and vertical height, you can also calculate area of a triangle using Heron's formula. This requires the length of all three sides of the triangle. According to heron's formula, the area of a triangle with 3 sides a, b and c is,
Area = square root of (p*(p-a)*(p-b)*(p-c)) (where p = (a+b+c)/2).
The following sample Java program calculates the area of a triangle given the length of its 3 sides. The following Java program also checks whether the given 3 sides can form part of a triangle. For a triangle, the sum of its 2 sides will always be greater than the third side.
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* Calculates area of triangle in Java given its 3 sides.
* @author jj
*/
public class AreaOfTriangle2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sn = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter length of first side of triangle:");
double a = sn.nextDouble();
System.out.println("Enter length of second side of triangle:");
double b = sn.nextDouble();
System.out.println("Enter length of third side of triangle:");
double c = sn.nextDouble();
AreaOfTriangle2 at = new AreaOfTriangle2();
if(at.isTriangleValid(a, b, c)) {
double area = at.calculateArea(a,b,c);
System.out.println("Area = "+area);
}else {
System.out.println("Sides entered cannot form a triangle!");
}
}
/**
* Calculates area of a triangle using length of its 3 sides
*/
private double calculateArea(double a, double b, double c) {
double p = (a+b+c)/2;
return Math.sqrt(p*(p-a)*(p-b)*(p-c));
}
/**
* Checks whether the 3 sides can form a triangle
* The sum of any two sides must be greater than the other side
* @param a
* @param b
* @param c
* @return
*/
private boolean isTriangleValid(double a, double b, double c) {
if((a+b)>c && (a+c)>b && (b+c)>a) {
return true;
}else {
return false;
}
}
}